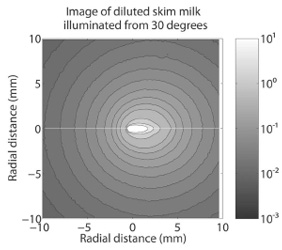
(a)
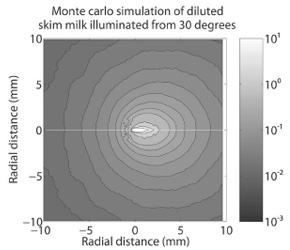
(b)
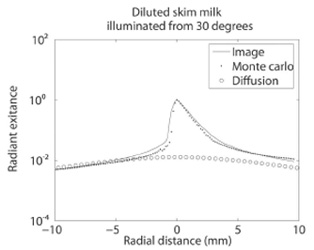
(c)
(a) Radiant exitance for the green color channel data from our skim milk measurement. (b) Fitting results using Monte Carlo Simulation with g = 0.7. (c) Intensity profiles for the central scanlines indicated with white lines in (a) and (b) and the result predicted by dipole diffusion.
Abstract
Many existing methods for the recovery of optical parameters from turbid materials rely on the diffusion approximation, which does not permit the recovery of the degree of anisotropy in the scattering phase function. These methods also make the explicit assumption that light is normally incident at the top surface of the material. We demonstrate a steady-state imaging technique that uses nonnormally incident light to determine anisotropy parameter g by fitting Monte Carlo simulation results to high dynamic range images of the intensity profiles of samples. The proposed method is simpler than existing methods and does not rely on thin samples to produce reasonable results.
Paper